ROC makes breakthrough in ionospheric research
Publication Date:01/28/2015
Source: Taiwan Today
A new scientific probe designed by Taiwan scientists is set to boost global ionospheric research while contributing to disaster prevention and enhancing the quality of satellite communications.
The Advanced Ionospheric Probe is the world’s first all-in-one sensor capable of measuring on a time-sharing basis ionospheric plasma concentration, temperatures and velocities over a wide range of spatial scales, according to Hsinchu City-based National Space Organization.
Designed by researchers from National Central University, AIP weighs 4 kilograms and measures 1,000 cubic centimeters, the lightest and smallest probe of its kind. It boasts a sampling rate of up to 8,192 hertz—the highest among all similar devices in operation—and will be installed on the Formosat-5 satellite set for launch early next year from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
Chao Chi-kuang, a key project member and associate professor of NCU Graduate Institute of Space Science, said since the ion probe on Formosat-1 commenced operations in 1994, the university’s researchers have published more than 100 papers based on related data and analysis. “AIP is certain to further strengthen Taiwan’s role as a provider of cosmological science data.”
According to Chao, the special electrode forming employed by the AIP sensor will significantly reduce electrode contamination and measurement errors, leading to better understanding of the characteristics of ionospheric plasma irregularities.
“This is important as the occurrence and density structure of plasma irregularities have a great impact on a variety of satellite communication-related applications, such as global positioning technology and national defense,” he said.
In addition, Chao said a recent study by NCU professor Liu Jann-yenq shows a likely correlation between changes in ionospheric variables and earthquakes. “The data collected by AIP will shed more light in this regard.”
Starting July, the NCU research team will offer project-related training sessions to senior high school students and select four to take part in the satellite launch.
Formosat-5 is the first homegrown space program fully overseen by the NSPO. It aims to build up Taiwan’s capabilities for independent development of spacecraft and payload instruments. (SFC-JSM)
Write to Taiwan Today at ttonline@mofa.gov.tw

NCU associate professor Chao Chi-kuang (left) and his research team are eagerly awaiting the launch of Formosat-5 and its AIP payload component. (Courtesy of NSPO)
メイドイン台湾の宇宙用観測機器「宇宙キューブ」、来年宇宙へ
Publication Date:01/28/2015
財団法人国家実験研究院(国研院)国家宇宙センター(NSPO)と国立中央大学は27日、初の国産となる宇宙用観測機器「先端電離層測定プローブ(AIP、Advanced Ionospheric Probe)」を発表した。まもなく地球観測衛星「FORMOSAT-5(フォルモサ5号)」に搭載され、宇宙天気と地震の前兆を観測する。
これにより、FORMOSAT-5は世界2基目の地震予知研究に貢献する衛星となる。
この機器は、外観がちょうど手のひらに載るほどの立方体で、「ルービックキューブ(中国語名=魔術方塊)」によく似ている。このため、「太空魔方(宇宙キューブ)」のあだ名で呼ばれている。重さは4キログラムと世界最軽量、最小の電離層測定プローブ。解像度も世界最高で、1秒にプラズマ8,000回余のサンプル取得が可能で、現在最も高性能の機器の9倍となっている。
FORMOSAT-5は来年第1四半期にも打ち上げられる予定となっている。
NSPOの劉正彦主席科学家によると、大地震が発生する1~5日前には、震源地上空の電離層でプラズマ濃度が際立って低くなるため、この状態を把握することで地震予知ができるようになる可能性もあるという。
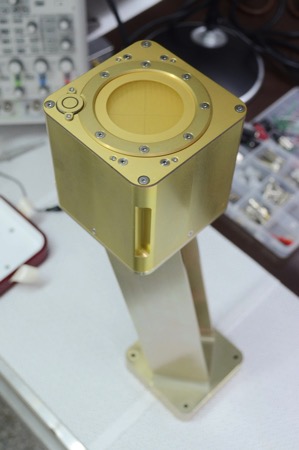
国家宇宙センター(NSPO)と国立中央大学が、初の国産となる宇宙用観測機器「先端電離層測定プローブ」を発表、来年第1四半期に打ち上げられる地球観測衛星に搭載される。(国研院提供、中央社)
